A gallstone is a stone made up of precipitated bile components that forms within the gallbladder. Cholelithiasis is the occurrence of gallstones or any condition induced by gallstones, whereas choledocholithiasis is the development of migrating gallstones inside the bile ducts. Gallstones are common in older and overweight people.
What to eat with gallstones? The formation of gallstones is the result of excessively fatty foods high in cholesterol. A healthy diet that avoids high fat foods will reduce the risk of gallstones for those in a healthy weight range. For needed fat in your diet, look for unsaturated fats.
Although the majority of gallstones can be avoided with a proper diet, a history of gallstones in your family history can still lead to their development. The risk of gallstones will always be present if this is the case, and you may need surgery for gallstones and the removal of a potentially perforated gallbladder.
Abdominal pain is the most common sign of gallstone inflammation, and there is a benefot for gallstone disease prevention during rapid weight loss for most types of gallstones. The development of gallstones can lead to sudden stomach aches and pains, so contact a health care professional if you’re concerned about gallstone formation.
What are Gallstones and Gallstone Symptoms?
The rates of gallstone disease varies from person to person. Generally however, diet is the root cause behind the incidence of gallstones. Diets which include more fibre and less fat in people with a lower, healthier BMI (such as plant based vegetarian diets) are associated with a lower risk for gallstones. Gallstones can be as small as a grain of salt, or large like a golf ball.
Around eighty percent of gallstones (four in five) are formed of pure cholesterol. That makes them the majority of gallstones and the cause of most gallstone pain. Still, there are two distinct types of gallstones present in diets of high fat products and high sugar products.
Choledocholithiasis, the majority of people will not get these gallstones. these stones get caught in your bile duct, preventing the movement of food and creating a painful obstruction. However, any and all conditions relating to a gallbladder attack is referred to as Cholelithiasis. However, of the types of gallstones obstructions in the ducts by gallstones cause more gallbladder pain.
Since gallstones are essentially solid obstructions, gallbladder pain is very common. This is called symptomatic gallstone disease, with the symptoms from gallstones occuring as stomach pain and inflammation. However, silent gallstones do exist even in a high fat diet.
Health professionals see assymptomatic gallstones in an unhealthy diet somewhat often. This is especially intense in a western diet, which tend to be fat and sugar centred. Fried foods, oil in food, cholesterol heavy foods, all of these can be trigger foods for sudden gallbladder pain, and gallbladder symptoms.
If your family history shows a history of gallstones, then treatment for gallbladder stones can vary. People with gallstones can live with them, avoiding foods that trigger a gallbladder attack and stomach pains. Gallstones don’t let the gallbladder contract to empty itself regularly, leading to a less than healthy gallbladder.
Chronic Gallbladder Disease

Gallstones and moderate inflammation are two symptoms of chronic gallbladder disease. The gallbladder may become damaged and rigid in such circumstances. Gas, nausea, and stomach discomfort after meals, as well as recurrent diarrhoea, are all symptoms of chronic gallbladder disease.
Losing or gaining weight rapidly can increase the risk of gallbladder disease. As such, if you want to avoid this risk of gallbladder disease then you should try and pace your weight loss or weight gain programme carefully. Otherwise, you may end up in some serious pain thanks to a fad “yo-yo” diet.
Poor diet is generally bad for your digestive health, according to most healthcare providers. The National Health Service in Britain reccomends a healthy, well balanced diet as the best preventitive measure to gallstones and gallbladder disease.
In a worst case scenario, you may suffer from gallbladder cancer. A family history, abdominal pain, poor diet, and gallbladder pain should all be indicators and signs that you should raise with a doctor or physician during a checkup, if you have concerns.
Although the gallbladder plays a semi-important role in the digestion of food, it can be removed via surgery. Much like the appendix and appendicitis, the gallbladder is not as much of a vital organ as other parts of your body like the heart and lungs.
What Does the Gallbladder do?
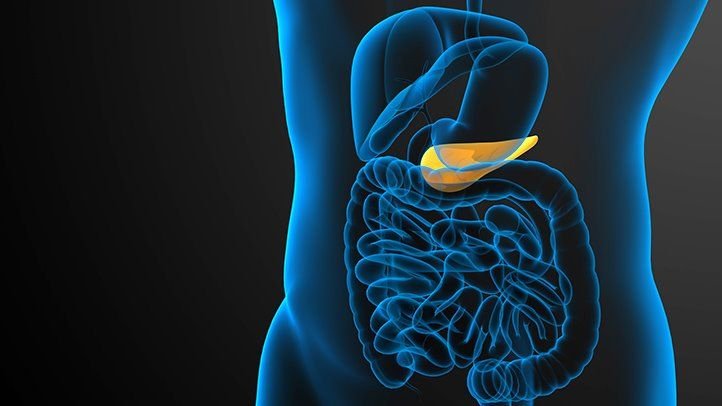
For the digestion of food, the small, pear shaped organ called the gallblader is responsible for the flow of bile and outflow of bile. While the liver is responsible for the production of bile, it’s the gallbladder that stores bile until it is needed.
Bile content is mostly cholesterol, which is why gallstones form from an excessive ingestion of cholesterol in varying amounts of food. However, the cholesterol in bile does complicate gallstones. Calcium and bile pigments can end up forming gallstones, in the absence of a poor diet.

A high fiber diet and a low fat diet can certainly help to keep your body healthy (gallbladder included). However, even if you don’t have a poor diet if you rapidly change body weight then you may produce less bile based sludge for people on these yo-yo diets.
This occurs in a small percentage of people, and in fact a large percent of people will generally lack any symptoms at all. To increase your understanding about health and the gallbladder, we reccomend the British National Health Service for further reading.
Bile salts travel down a bile duct, where the bile then turns into fatty acids designed to help breakdown and digest fatty foods in the intestine and stomach. Naturally gallstone obstructions of the bile duct are not only painful, but prevent the bile duct from allowing bile to digest fattier foods properly.
Other Gallstone Treatments
Healthy foods are one thing, but a poor diet is only the root cause of most gallstones. Some, in fact, come from a family history, making the abdominal pain even worse. In these recurrent cases, you may undergo surgery to remove your gallbladder entirely, and whatever types of gallstones you had with it.
The majority of gallstones are recurrent, but this is thanks to the resumption of a poor diet by the majority of people. A study by researchers has found the overwhelming majority of gallbladder surgeries have gallstones returning within a few months.
A hospital based case control study did find a link between vegetable proteins and a reduced risk of gallstones. This vegetable protein, found in anything from garden veg such as onions to beans, can be a good way to improve your diet.
Things to Cut Out
So, if you have gallstones, what should you eat? To begin, you should limit your intake of high-fat, high-cholesterol meals, which might cause gallstones in the first place. The easiest method to do this is to eat a low-fat, high-fiber diet. The idea is to avoid items that cause pain and discomfort, which typically means staying away from fatty and fried foods.

Cutting out fatty meals to get in meals with vegetables should sound fairly obvious. However, it is the cholesterol containing and artery clogging saturated fats that you should be actively trying to remove from your diet. Fat cheeses, full fat milk, and heavy creams can all contain saturated fats.
Try to find reduced fat or lighter products. A reduced fat product can contain anywhere between 25 to 75% less fat than the original product, and often keeps the same great taste and texture you are used to enjoying with your dietary needs.
For milk, try skimmed or semi skimmed milk alternatives. Milk containing non-animal products such as almond milk and oat milk are also healthier. Avoid full fat cheese, and instead choose soft cheeses. Reduced fat cheddar cheese and cottage cheese are also great tasting substitutes.
Low fat evaporated milk tends to have a longer shelf life, although it can be an aquired taste. If you dislike the taste of low fat evaporated milk, then skimmed or semi skimmed milk keeps more of the creamy texture.
Similarly, if you dislike the texture of soft cheeses and cottage cheese, then replace your full fat cheese with a reduced fat cheddar cheese. Thanks to the boom in health conscious diets, as well as vegetarian and vegan diets, you will have plenty of options to enjoy.
Meat pies might be replaced by lean meat instead. Cuts of meat can get quite excessively fatty, so always removed the visible fat and skin from meat when cooking. White fish is also a good source of protein that will not negatively affect your gallbladder health.

If you are on a low-carb diet and have gallstones, you may be in some pain and wondering what you can eat. The good news is that you can still eat lean meat. For instance, chicken thighs with the skin taken off are very low in carbohydrate. If you want to get even more lean meat, you could choose a pork chop or some lean ground beef.
How to get a Healthier Gallbladder?
Brown rice is a great source of fibre and that mythical vegetable protein we discussed earlier. Food preparation goes a long way when it comes to improving digestive health, so including brown rice over white rice in your meals can do great things.
Refined carbohydrates can help to reduce gallstone inflammation, and gallbladder pain. Compared to the original product, refined carbs can be a far healthier alternative that also tend to be keto friendly. Since up and down weight loss and gain from diets can cause gallbladder pain, then this is a fine substitution.

Low-fat dairy products, as previously mentioned, are always helpful in promoting gallbladder health. However, since saturated fats are the root cause you should also monitor your oil when cooking. Roughly a teaspoon per person is an aceptable volume of oil.
Alternatively, try unsaturated healthy fats in certain oils. Olive oil, canola oil, and even fish oil are considered healthy fats that will actually help your gallbladder flush and empty on a regular basis. A perfect solution as fish tinned in oil is commonly available on store shelves.
Fish is a great source of lean protein and omega-3 fatty acids, as well as a host of vitamins and minerals. For people with gallstones, there is some debate about whether fish is a good choice. For the most part, fish is generally considered safe for people with gallstones.
Fruits should be consumed fresh. They’re fantastic for removing gallstones. Because of the natural fibre and water in the fruits, they are an excellent way to wash out gallstones. The high fibre content of most fresh fruits contributes to that fibre level, which can be difficult to achieve on something like a gluten-free diet.
Vegetables, in general, are low in fat and are less likely to trigger gallbladder disease symptoms than high fat diets. A variety of vegetables have been demonstrated to protect the gallbladder and reduce the chance of gallstones or a flare-up of gallbladder disease.

